|
Why India Needs to
Enhance
Use of Construction Sector Waste
How MSMEs can help towards transition to a Green Economy?
India’s share in the world population is 17.7% . The country’s
population was 377 million in 1950, and is expected to grow to 1.5
billion in 2030 and 1.6 billion by 2047 , making it the most populated
nation in the world. Further, there will be an addition of 404 million
urban dwellers by 2047. To meet the demand of the population for basic
amenities, inclusive smart cities with urban infrastructure are
required.
The construction sector in India is one of the integral industries and
the second largest after agriculture. It contributes 8% of India’s GDP
and is expected to grow at an annual average of 6.6% until 2028 . India
is slated to become the third largest market in the world for
infrastructure and construction activities by 2025. The sector is one of
the largest employers in this country, employing around 49.8 million
people. The exact number is difficult to ascertain as the sector is
highly fragmented with unorganised players contributing highly.
India consumes 7.2% of globally extracted raw materials (fossil fuels,
metals, non-metals and biomass), with the construction sector using a
major portion of this. Looking at the rate of construction growth,
meeting the material demand is a daunting challenge. Further, the use
and disposal of construction and demolition waste – composed of bulky
materials such as concrete, stone, brick and mortar – is still not
streamlined. The recoverable items such as metal rods, pipes and
fixtures are salvaged by the informal sector. Use of C and D waste in a
sustainable manner would not only reduce the burden on virgin materials
but also prevent myriad environmental and social problems caused by it.
With rapid population and urbanisation, the waste generation is expected
to increase multi-fold. It is expected that 70% of buildings that will
be existing by 2030 are yet to be built. The Smart Cities scheme
launched by the government in 2015 promotes sustainable and inclusive
development by application of Smart Solutions. Currently 100 cities have
been selected for the programme that strategises to improve the cities
by redevelopment, retrofitting and expansion in a sustainable manner to
improve quality of life of citizens. The renovation and redevelopment of
housing and infrastructure under the Smart Cities Mission will increase
the demand of building materials and at the same time will generate C
and D waste, which would contribute to a third of urban waste. In India
reuse of C and D waste has already been very low and the additional
burden of this waste to be generated in the coming decades could be a
major challenge for the country.
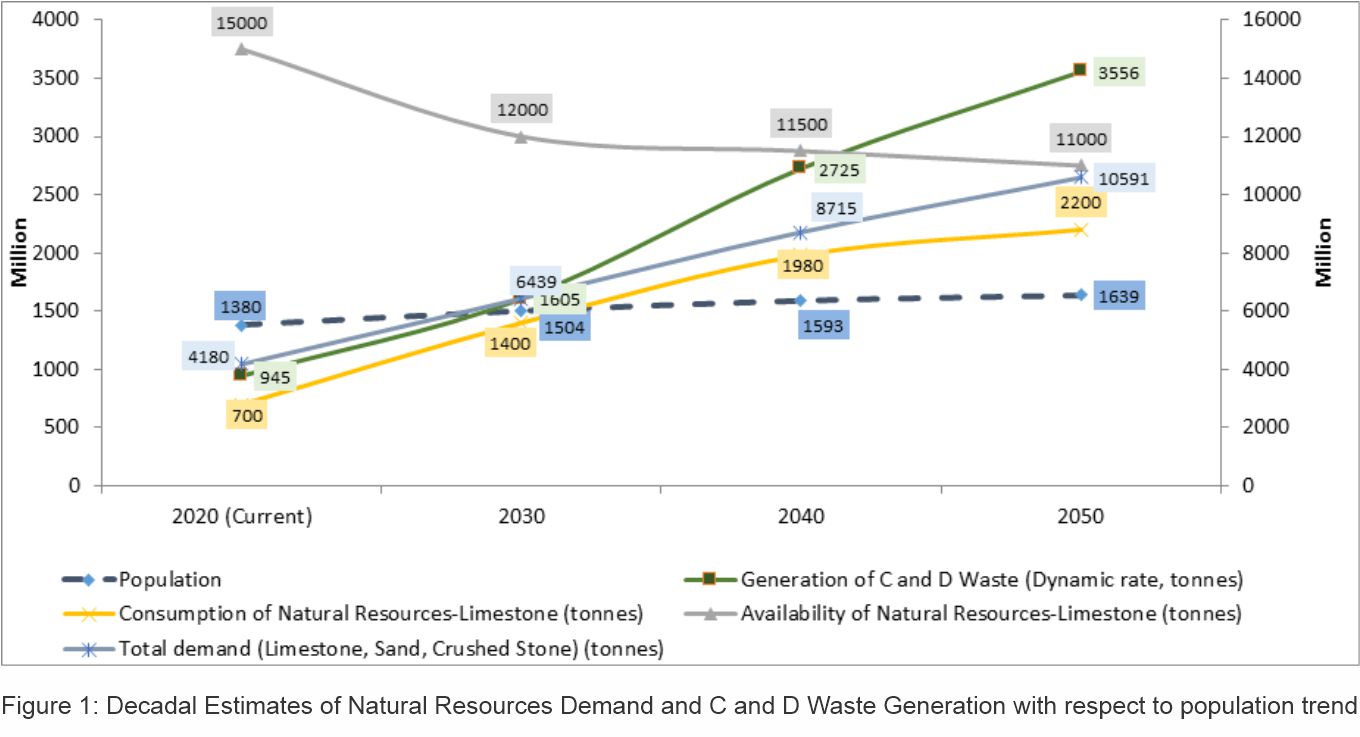
The existing challenges of rapid population growth, declining reserves
of minerals, demand for minerals for next generation of new housing
units and increase in C and D waste generation (see Figure 1) has put
stress on the ecosystem. The decadal projections made for C and D waste
generation based on the exponential growth rate shows that the number
will increase by 73% from 2020 to 2050 while the availability of
limestone reserves are expected to decline by 26.7% based on the rate of
current use. The demand of materials used for construction (limestone,
sand, crushed stone) is expected to rise by 35% by the next decade and
60% by 2050. Thus, given the increasing demand of materials in the
construction sector by the increasing population of the country and the
deficit in reserves expected due to high demand, technological
innovations are needed in the sector to use waste materials in a
sustainable manner. The use of C and D waste with a holistic approach
with the support of civil society, building contractors, real estate
developers, government stakeholders and entrepreneurs could be a viable
option.■
References:
-
https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/india-population/
(Website Accessed on 06 April 2020)
-
Utilisation of Recycled Produce of Construction and Demolition Waste: A
Ready Reckoner (BMTPC, 2018)
-
https://www.populationpyramid.net/india/2047/ (Website Accessed on 07
May 2020)
-
https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/publications/2014-revision-world-urbanization-prospects.html
(Website accessed on 29 April 2020)
-
https://www.makeinindia.com/sector/construction
(Website Accessed on 06 April 2020)
-
https://www.indiaservices.in/construction (Website Accessed on 30 April
2020)
-
Reference Report for Integrated Resource Efficiency Policy for India
(TERI, 2019)
-
MoHUA.
Strategy for Promoting Processing of Construction and Demolition (C&D)
Waste and Utilisation of Recycled Products (2018)
-
Material Consumption
Patterns in India A Baseline Study of the Automotive and Construction
Sectors (GIZ, 2016)
Neha Agarwal
nagarwal@devalt.org
Back to Contents
|
