|
Jal-TARA Arsenic Kit
Ground water is an important source of domestic water in West Bengal and Bangladesh, but it is now clear that much of the ground water in these areas is contaminated with naturally occurring arsenic. Out of 20 countries in different parts of the world where ground water arsenic contamination and human sufferings have been reported so far, the magnitude is considered highest in Bangladesh, followed by West Bengal. About 6 million people in West Bengal and 25 million in Bangladesh are at present drinking water contaminated with arsenic at a level above 50ppb.
Sources of arsenic pollution Arsenic is a naturally occurring element in the earthís crust. It occurs as a major constituent in more than 200 minerals, including elemental arsenic, arsenides, sulphides, oxides, arsenates and arsenites. In West Bengal and Bangladesh, it is believed that arsenic is largely due to the erosion from local rocks. Increased ground water extraction has caused this problem by dropping the ground water level in much of the region.
Effected locations High concentrations of arsenic have been reported in eight districts of West Bengal and one district each from Bihar and Madhya Pradesh. Bangladesh is also adversely affected by high arsenic content in ground water. Out of a total of 188 million people in West Bengal and Bangladesh, 136 million people live in arsenic affected districts where ground water contains arsenic level above 50ppb. Detailed description of arsenic affected areas and population in West Bengal and Bangladesh are given in the table provided below.
Guidelines and Standards Impacts of arsenic contamination
The main
arsenic ingestion mediums are drinking water, food and road side dust,
while contribution of road side dust is very small; the other two play a
very-very important role. Long term ingestion of high arsenic
concentration (>50ppb) water results in Arsenicosis,
Hyperpigmentation, Depigmentation, Keratosis and
peripheral vascular disorders are the most commonly reported symptoms of
chronic arsenic exposure. It is estimated that in West Bengal two
million people are at health risk due to ingestion of arsenic water. Status of monitoring and Surveillance efforts The major challenge is how to rapidly reduce and monitor the arsenic consumption of millions of people scattered over a huge area. The respective governments, external support agencies and non-governmental organizations are already pooling their resources to determine the extent of ground water contamination, and develop long term solutions to the problem. However, it has been estimated that it may take 10 to 15 years to provide sustainable arsenic free water supply options to all the threatened areas.
One of
the current priorities is to check existing tube wells for arsenic
contamination, and to set up sustainable arsenic monitoring systems. In
addition arsenic removal technologies need to be monitored to ensure
that arsenic is consistently removed to below permissible limits. Need for extensive monitoring Arsenic is poisonous even at extremely low concentrations. Standards for safe levels of arsenic in drinking water vary from around five parts per billion to 50 parts per billion. The standard set by WHO is 0 parts per billion and BIS is 50 parts per billion. Thus, devices that can reliably measure arsenic down to these levels are essential.
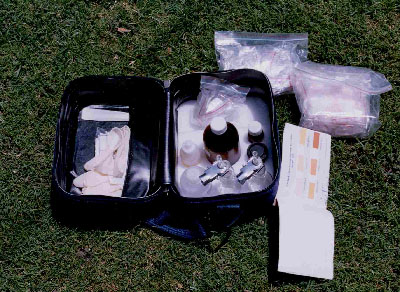
Development Alternativeís initiative
Keeping
all this in view, the Environment Systems Branch at Development
Alternatives has developed an Arsenic field testing potable kit for
determining the presence of Arsenic and proper monitoring.
Salient
Features of the kit
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||