|
Environmental
Assessment of VSBK, Datia EBV Kumar and Dr K Vijaya Lakshmi The Vertical Shaft Brick Kiln (VSBK) technology, first developed in China, is environment friendly and energy efficient. Environmental assessment of VSBK was carried out by the Environment Systems Branch of Development Alternatives (DA) in Datia, Madhya Pradesh. The results of the environmental assessment are given below: T he most prevalent technologies in the Indian subcontinent for burnt brick production include Bull’s Trench, Hoffman and Clamp
technologies. Bull’s Trench Kiln (BTK), with a moveable and fixed
chimney, is the most widely used technology because of its high
energy efficiency and large scale of production. But BTK technology
suffers from its poor environmental performance with respect to air
emissions. In a recent notice, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
recommended the phasing out of moveable chimney type kilns of BTK by
December, 1997. production include Bull’s Trench, Hoffman and Clamp
technologies. Bull’s Trench Kiln (BTK), with a moveable and fixed
chimney, is the most widely used technology because of its high
energy efficiency and large scale of production. But BTK technology
suffers from its poor environmental performance with respect to air
emissions. In a recent notice, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
recommended the phasing out of moveable chimney type kilns of BTK by
December, 1997.
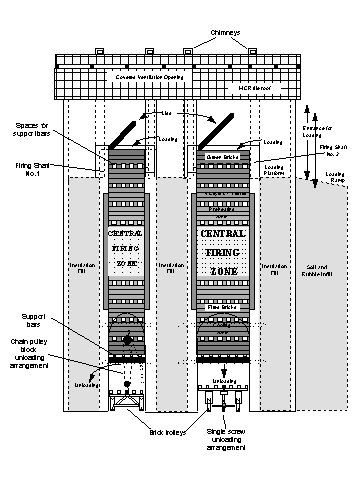
To try out an alternative, energy efficient and environmental friendly technology for burnt brick production, DA and the Tata Energy Research Institute (TERI) undertook this study of adaptation of VSBK in India (see photograph below) with support from the Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC). The principle of operation in VSBK is that a continuous chain of green bricks loaded from the top passes through a centrally located firing zone in a rectangular vertical shaft and comes out as fired clay bricks from the bottom. These kilns are very similar to the vertical shaft lime kilns. Fresh green bricks are shifted to the top loading platform, using donkeys along the ramp. These green bricks are loaded at the top in batches after every two hours and they are lowered down slowly through the firing zone which is located at the centre of the shaft. Each batch stays in the firing zone for nearly two hours and is then slowly moved down along the shaft in a step wise unloading process after every two hours (Refer Fig.1). Need for Environmental Assessment VSBK is a widely operating, energy efficient technology for burnt brick production in China. Such energy efficient technologies emit less pollution into the environment due to less consumption of fuel. Presently available technologies like BTK, Hoffman and Clamps are highly polluting technologies. In order to check the relative environmental friendliness of VSBK and to compare against BTK and Clamps, an environmental assessment was carried out in Datia. Since VSBK is a small scale production technology with good energy efficiency, there is a danger that more units may come up in an area, which in turn may cross the assimilative capacity of that area. In order to reduce the unit rate of emissions from VSBK, cleaner production measures can be suggested through environmental assessment. Waste Generation Sources In a burnt brick production, the main types of waste generation include : air emissions, coal ash and broken fired bricks. Air emissions are mainly from the chimneys, top opening of the shaft and from the bottom of the shaft. As the movement of fire is in an upward direction, naturally the gaseous emissions will be very little at the bottom portion of the shaft. The fuel used in VSBK is powdered coal. Due to complete burning of coal, only a small amount of ash comes out as waste. Breakage of bricks takes place due to uneven loading and unloading, over burning in one batch, and due to mechanical impact while unloading the bricks. The percentage of broken fired bricks is very little (3 per cent to 4 per cent) in VSBK as the number of bricks in each batch are relatively few. Environmental Assessment and Monitoring Objectives An environmental assessment was carried out on VSBK in Datia for two types of clay bricks i.e Datia clay and Bhognipur clay. Datia clay bricks are tried with total internal coal and partial internal coal as fuel. The monitoring objectives for VSBK are to :
Methodology All the monitoring carried out at Datia was based on the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) or Environment Protection Agency (EPA) standard methods. The dust measurements were carried out using gravimetric analysis. SO2 and NOx were analysed using spectrophotometric methods. The ambient and work place concentrations were measured using the High Volume Sampler (HVS) and Respirable Dust Sampler (RDS-Envirotech 415) manufactured by Envirotech. The stack emission measurements were carried out with a stack monitoring kit of Netel Chromatographs. As the purpose of the study is for performance evaluation of the VSBK technology, the ambient samples and work place were monitored for four hours duration. Total monitoring was carried out for 192 hours. Stack emissions were monitored for 40 minute duration to collect one m3 of air in each sample with a stack monitoring kit. Total stack monitoring was carried out for 25 hours. Velocity was measured using Envirotech S-type pitot tube (APM-620). Due to very low velocities (2-3 m per second) in the chimney, a differential manometer is used with a water and aniline junction as an indicator for the pitot tube readings. Temperature was measured using an Envirotech pyrometer (APM-620). Environmental Standards The
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) supervises and regulates the
As the VSBK technology is very similar to Vertical Shaft Lime Kilns and also the production capacity is between 5 T / day to 40 T / day, we can adopt the standards of 500 mg/Nm3 as particulate emission standard till there is a fixed standard specified for VSBK. Recently the CPCB has come out with emission standards for Particulate Matter (PM) for BTKs. Table 2 shows the emission standards for Particulate Matter in BTKs. The notification of "The permissible levels of certain chemical substances in work environment" by the Ministry of Labour on July 22,1988 can be adopted as a standard for work place environment of VSBK. Table 3 shows the notified standards for relevant substances. Results of Environmental Quality Monitoring During the course of monitoring, several improvement measures such as height of chimney, increase in number of brick stackings, provision of lid on the shaft in the working platform, improvement of ventilation in the work place, etc. were identified and implemented. The final monitoring results of VSBK are provided in table 4. Inferences from Monitoring Results The inferences from the monitoring results are : a) Work Environment Monitoring
Acknowledgement We wish to acknowledge the contribution of other team members, P Ratna Prasad, Parmod Kumar and S.N Prasad, who played a major role in undertaking this study. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 environmental standards in India. CPCB has evolved two types of
specifications viz emission standards (for emissions from the
chimneys) and ambient air quality standards (outside the factory
boundary wall). Generally emission standards are industry specific,
depending on the type of process, technology and capacity of the
industry. As VSBK is a new technology, there are no specified
emission standards. In the discussions we had with CPCB scientists,
it was suggested to compare the emissions of VSBK with emission
standards of similar technology and similar scale of operation.
VSBK technology is very similar to vertical shaft lime kiln
technology. Table 1 shows the emission standards for lime kilns.
environmental standards in India. CPCB has evolved two types of
specifications viz emission standards (for emissions from the
chimneys) and ambient air quality standards (outside the factory
boundary wall). Generally emission standards are industry specific,
depending on the type of process, technology and capacity of the
industry. As VSBK is a new technology, there are no specified
emission standards. In the discussions we had with CPCB scientists,
it was suggested to compare the emissions of VSBK with emission
standards of similar technology and similar scale of operation.
VSBK technology is very similar to vertical shaft lime kiln
technology. Table 1 shows the emission standards for lime kilns.